One cannot discuss the world of art without acknowledging the profound impact and rich history of African art. From the ancient cave paintings of Algeria to the intricate sculptures of the Benin Kingdom, Africa has always been a treasure trove of artistic ingenuity. These traditional art forms have not only captured the essence of the continent’s diverse cultures but have also left an indelible mark on the global art scene.
In the modern world, technology has become an omnipresent force, radically transforming various industries and shaping the way we live, work, and create. Art, too, has been swept up in this wave of innovation, with artists around the globe employing cutting-edge tools and techniques to push the boundaries of creative expression. It is in this thrilling context that we explore the ways in which African artists are embracing technology to create innovative art forms, reshaping the continent’s cultural landscape and amplifying its global influence.
The fusion of traditional African art and technology
African artists have long been recognized for their ability to adapt and evolve, drawing on the rich tapestry of their cultural heritage while also embracing new ideas and influences. In the digital age, this adaptability has taken on a new dimension, with many artists skillfully merging traditional art forms with digital mediums to create a unique and captivating aesthetic.
For instance, Nigerian artist Laolu Senbanjo has gained international acclaim for his distinctive “Afromysterics” style, which combines elements of traditional Yoruba mythology with modern digital painting techniques. Senbanjo’s work has been featured in galleries and exhibitions around the world, as well as on the bodies of celebrities like Beyoncé in her visually stunning music video for “Lemonade.”
Another example is the rise of virtual reality (VR) experiences that transport users into immersive, interactive worlds inspired by African stories and myths. Kenyan filmmaker Ng’endo Mukii’s VR film, “Nairobi Berries,” weaves a poetic narrative that explores themes of identity and belonging against a backdrop of traditional African folklore, while South African studio BlackRhino VR’s “The Lost Botanist” invites players to unravel the secrets of a fantastical world steeped in African botanical mythology.
The fusion of traditional African art and technology not only breathes new life into age-old artistic practices but also offers significant advantages in terms of cultural preservation and accessibility. By digitizing and sharing their work online, African artists can ensure that their cultural heritage is safeguarded for future generations while also reaching a wider, more diverse audience than ever before.
Technological innovation as a driving force for new African art forms
The rapid pace of technological innovation has also spurred the emergence of entirely new art forms, with African artists at the forefront of these exciting developments. Social media, in particular, has played a pivotal role in connecting artists across the continent and beyond, fostering collaboration, exchange, and experimentation on a scale previously unimaginable.
Ghanaian artist Ibrahim Mahama, for example, has harnessed the power of social media to gain international recognition for his large-scale installations using jute sacks, a material that carries deep historical and economic significance in West Africa. By sharing his work on platforms such as Instagram, Mahama has been able to engage with curators, collectors, and fellow artists around the world, culminating in prestigious exhibitions at venues such as the Venice Biennale and London’s White Cube gallery.

As technological breakthroughs continue to emerge, African artists are seizing the opportunity to push the boundaries of their craft even further. 3D printing has revolutionized the field of sculpture, allowing artists like South African Lionel Smit to create intricate, multi-layered works that blend traditional techniques with cutting-edge digital design. Smit’s “Morphous” series, for example, explores themes of identity and transformation through a series of striking, larger-than-life bronze sculptures, each one painstakingly constructed from thousands of 3D-printed fragments.
Augmented reality (AR) and interactive installations have also opened up new avenues for artistic expression, with African artists harnessing these technologies to create immersive, multi-sensory experiences that challenge conventional notions of art. Kenyan artist Wangechi Mutu’s AR installation, “The NewOnes, will free Us,” invites viewers to interact with a series of otherworldly figures that come to life through a smartphone app, while Nigerian artist Olalekan Jeyifous’s “Mad Horse City” uses AR to explore the future of urban planning in a dystopian, post-apocalyptic Lagos.
The realm of artificial intelligence (AI) and generative art has likewise captured the imagination of African artists, who are using these technologies to create compelling, thought-provoking pieces that blur the line between human and machine creativity. Moroccan artist Sougwen Chung’s “Drawing Operations” series, for instance, features a robotic arm that “collaborates” with the artist in real-time, producing intricate, abstract drawings that are part human, part machine.
The role of technology in addressing social and environmental issues through African art
As African artists continue to embrace the possibilities offered by technology, they are also using their work to tackle pressing social and environmental issues. Art has long been a powerful medium for raising awareness and sparking debate, and in the digital age, its potential to effect change is even greater.
A notable example is the work of Nigerian artist Uche Uzorka, who employs digital collage techniques to address themes of inequality, migration, and gender in his thought-provoking pieces. By juxtaposing images from various sources, Uzorka creates striking visual narratives that challenge viewers to confront the complex realities of contemporary African society.
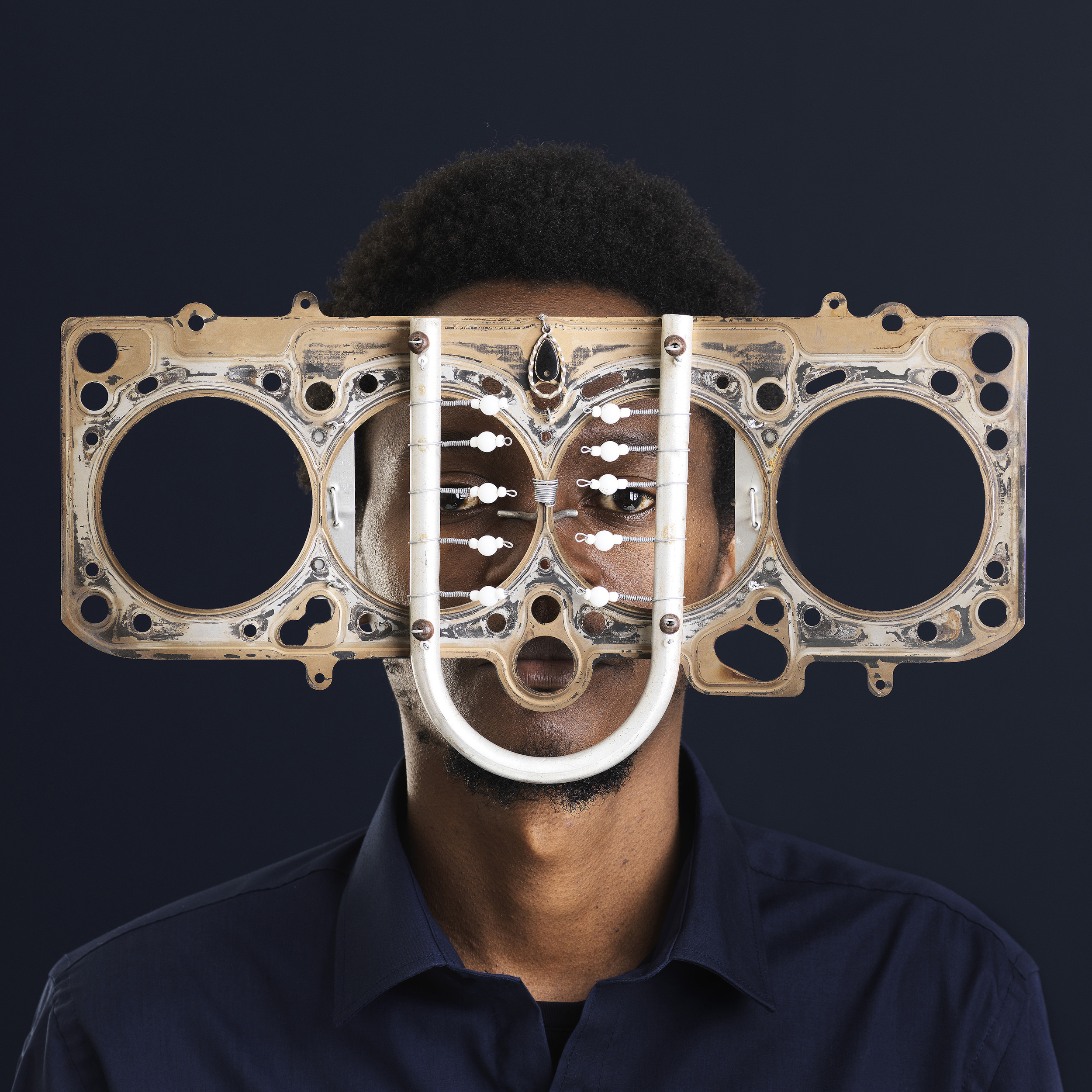
African artists are also turning their attention to the issue of sustainability, employing innovative, eco-friendly techniques and materials in their work. Kenyan artist Cyrus Kabiru, for example, creates stunning, futuristic eyewear sculptures from discarded electronic waste, highlighting the urgent need for responsible consumption and waste management. Similarly, South African artist Mbongeni Buthelezi uses melted plastic bags to “paint” intricate, textured scenes that not only showcase the beauty of his homeland but also raise awareness about the environmental impact of single-use plastics.

In conclusion, the creative synergy between African artists and technology is not only revitalizing the continent’s artistic heritage but also paving the way for a vibrant and innovative future in the world of art. From the fusion of traditional African art forms with digital mediums to the emergence of entirely new artistic practices driven by cutting-edge technologies, African artists are pushing the boundaries of what is possible, reshaping the cultural landscape and amplifying their global influence.
As we look to the future, it is clear that the ongoing transformation of the African art scene will continue to captivate and inspire, with technology playing an ever-greater role in the evolution of artistic expression. And as African artists continue to harness the power of technology to address social and environmental issues, their work will not only serve as a testament to the continent’s boundless creativity but also as a catalyst for positive change in the world.
Ultimately, the marriage of African art and technology is a testament to the resilience, adaptability, and ingenuity of the continent’s artists. In this rapidly changing digital landscape, their pioneering spirit and innovative vision serve as a beacon of inspiration for all who seek to create, explore, and reimagine the possibilities of human expression.




 No products in the basket.
No products in the basket.